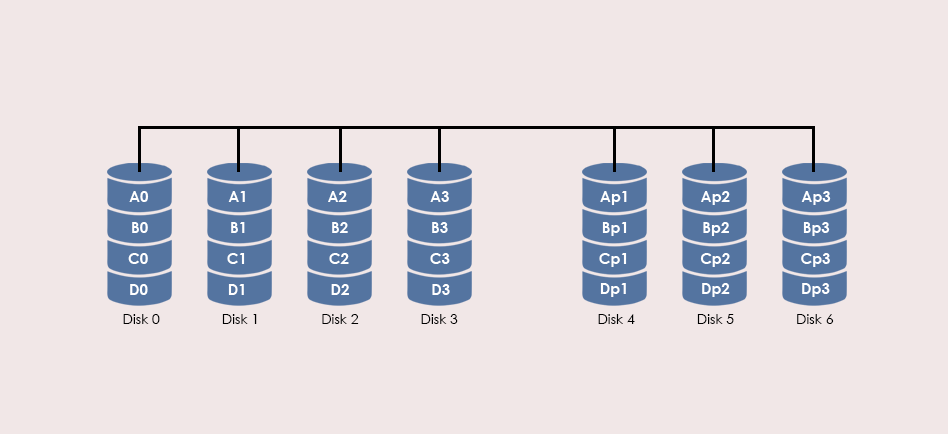
Characteristics & Advantages
- Extremely high data transfer rate
- Disk failure has an insignificant impact on throughput
- Low ratio of ECC (Parity) disks to data disks, that means high efficiency
Disadvantages
- Cannot handle simultaneous requests
- Internal error correction complexity of the Hamming Code, offers little advantage over parity.
- RAID 2 is rarely implemented for commercial purpose
Recommended Products