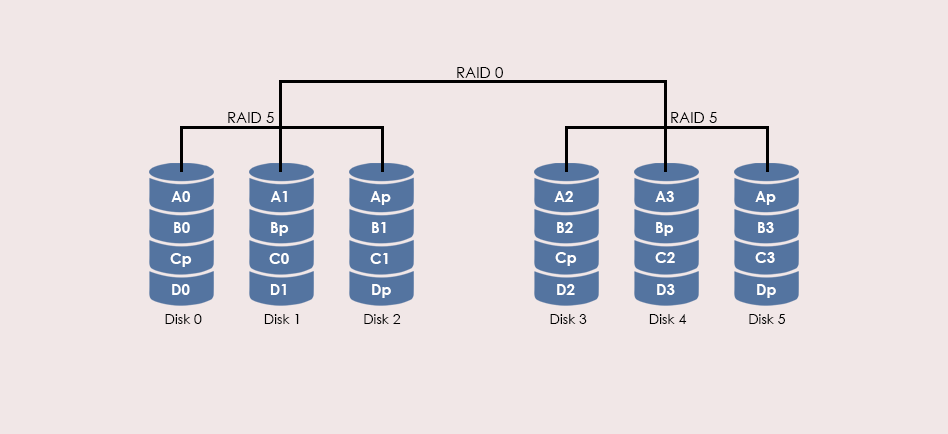
Characteristics & Advantages
- RAID 50 improves upon the performance of RAID 5 particularly during writes
- Provides better fault tolerance than a single RAID level.
Disadvantages
- Implementation is very expensive
- Compared to RAID 5 parity overhead, the RAID 50 overhead is the multiple of the number of RAID 5 segments
- Failure of two drives in one of the RAID 5 segments renders the whole array unusable
Recommended Products
Recommended Applications
- Applications that require high fault tolerance, capacity and random access performance