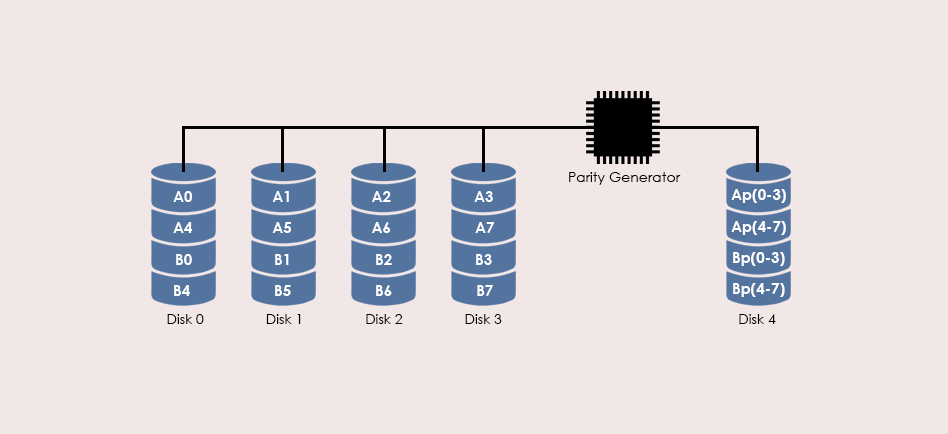
Characteristics & Advantages
- Very high Read and Write data transfer rate
- Insignificant impact on throughput due to disk failure
- The ratio of Parity disks to data disks is low, which means higher efficiency
Disadvantages
- Transaction rate equal to a single disk drive at best
- Controller design is fairly complex
- Very difficult and resource intensive as a software implementation
- Cannot provide service in multiple requests simultaneously
Recommended Products
Recommended Applications
- Image and Video Editing
- Live streaming
- Prepress Applications
- Any application that require high throughput