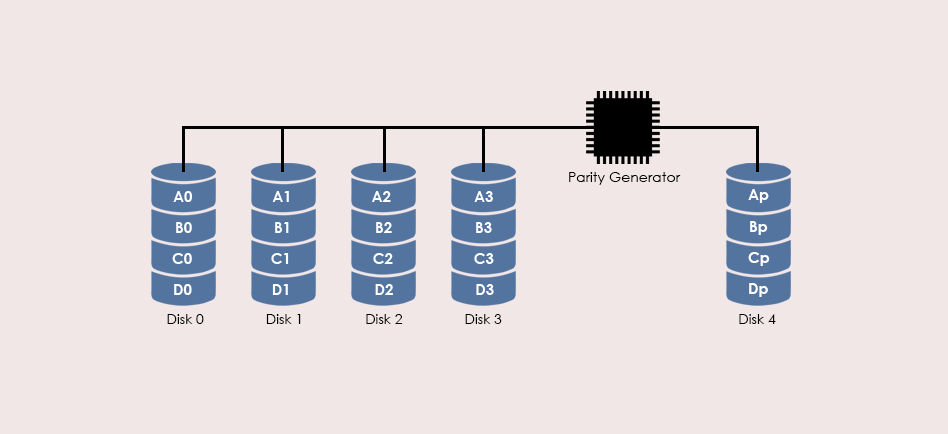
Characteristics & Advantages
- Very high Read data transfer rate
- High random read rate
- The ratio of Parity disks to data disks is low, which means higher efficiency
Disadvantages
- Controller design is fairly complex
- Worst write transaction rate
- Data rebuild is difficult and inefficient during disk failure
Recommended Products
Recommended Applications
- Video Production and live streaming
- Image Editing
- Video Editing
- Prepress Applications
- Any application requiring high throughput